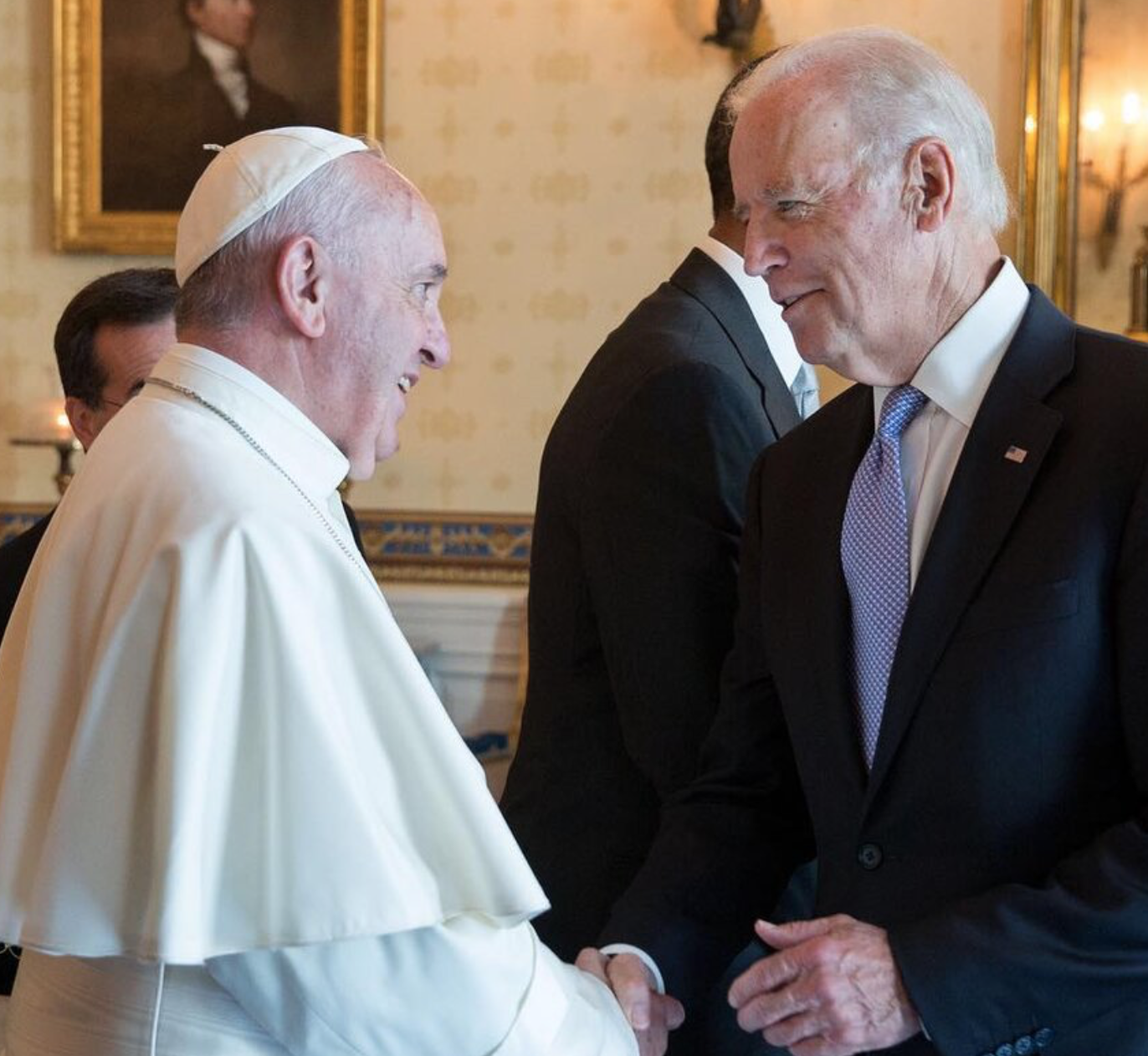
I have to admit that I experienced a sense of excitement, mixed with dread, when I saw the following headline this weekend, care of the Gannett wire here in Tennessee: “Why is Three Kings Day celebrated? Epiphany? And what does Rosca de Reyes have to do with king cakes?”
Most of the time, the contents of The Knoxville News Sentinel is dominated by University of Tennessee sports, coverage of bad Republicans doing bad things and updates about business and real-estate news in downtown neighborhoods favored by hip readers.
Coverage of the Feast of Epiphany — which follows the oft forgotten 12 days of Christmas — had the potential to offer unique details about traditions in local churches. But stories about Christian holy days are hard for many newsrooms, since they involve lots of picky facts about, you know, “religious stuff.”
OK, so what is wrong with this lede?
People around the world will celebrate Three Kings Day this weekend.
That lede could have said “Christians” and that would be vague, but OK. But, “people”?
Let’s keep reading, because things get a bit better and also rather strange at the same time.
In Hispanic communities, the day is known as Día de Los Reyes and is celebrated on Jan. 6 which is Saturday this year. The day is meant to honor the story revolving around the Three Wise Men or Magi who came to bring baby Jesus gifts after his birth. For those of the Christian and Catholic sects, it is known as the Epiphany.
The Hispanic reference is helpful, since Día de Los Reyes is a big deal and it’s totally appropriate in many zip codes to stress that. But what, in heaven’s name, is the point of this: “For those of the Christian and Catholic sects, it is known as the Epiphany.”
Think about that for a second. Catholicism is a “sect,” as opposed to being the world’s largest ancient Christian communion? And what are the other “sects” we are talking about here?