We can expect that the U.S. House select committee investigating the Jan. 6 Capitol attack will unveil findings in time to help Democrats' Nov. 8 prospects and, thus, spur Republican ire.
Even if the report ignores the matter, this report can peg thoughtful and thorough journalistic re-examination of the religious significance of continuing furor over the nine troublesome weeks from the 2020 vote through Jan. 6. Carefully balanced, non-partisan contexting will be needed.
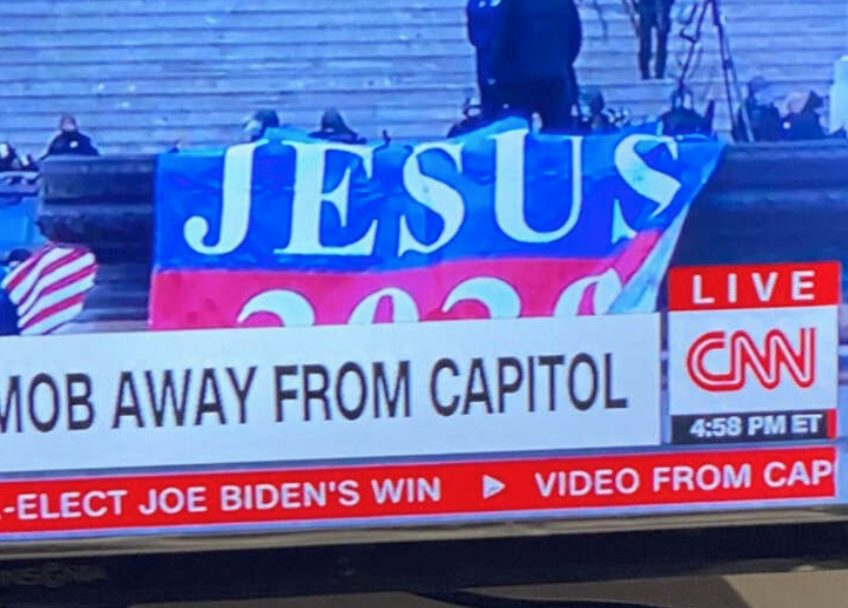
Media and amateur videos show us that – yes – some of the rioters uttered prayers and brandished Christian signs, slogans and symbols. Were they isolated cranks, or representative of a broader religious phenomenon, or a bit of both?
A New York Times anniversary walkup last week counted 275 defendants with federal charges for obstructing Congress, 225 or so for acts against police, and another 300 for minor trespass or disorderly conduct. So far, a fifth of these defendants have admitted legal guilt.
Importantly, the Times reported that the mob included "church leaders" (plural).
In a national newspaper, that phrase suggests not some small-time parsons from independent churches but notable media stars, denominational and "parachurch" officials, influential college and seminary thinkers, or at least local pastors from "big steeple" congregations. In fact, that reference appears to echo this Times passage that has been discussed several times here at GetReligion, referring to religious image on Jan. 6:
The blend of cultural references, and the people who brought them, made clear a phenomenon that has been brewing for years now: that the most extreme corners of support for Mr. Trump have become inextricable from some parts of white evangelical power in America.
At some point, it would be good to cite examples of “church leaders” linked to “evangelical power.”
By contrast, last year The Washington Post's Michelle Boorstein perceptively profiled certain of the rioters to highlight Americans' growing trend of concocting idiosyncratic "do it yourself" religions for themselves.